Help for Postural Pain after Breastfeeding
International Journal of Childbirth Education. March 2009
Heather Jeffcoat, DPT
One of the most precious bonds between a mother and her new baby is sharing the closeness of nourishing her child. Whether this occurs by breast or by bottle, there is nothing that compares to holding that little baby close, looking into their eyes and taking in that sweet baby scent. Over time, with poor positioning of her infant and adaptive postures that the mother will take on, musculoskeletal pain may develop. The most common place to develop these aches and pains are in the neck, upper and mid-back regions. They can be as mild as a dull ache felt between the shoulder blades to a debilitating tension headache that can make it difficult to care for her child.
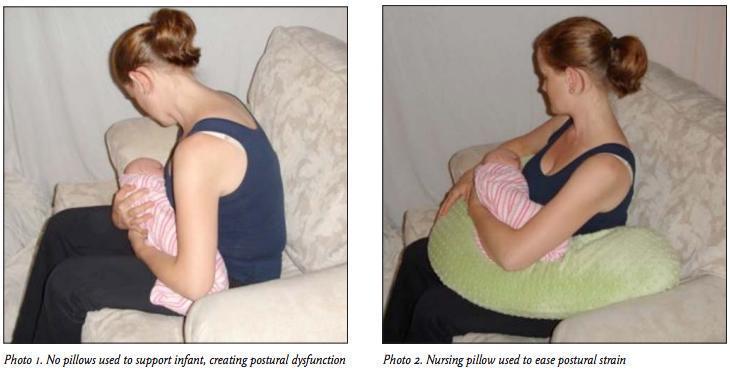
With nursing and bottle-feeding, it is important that the child be supported to minimize the requirement of the mother to round her shoulders forward, slump her back and dropping her head forward (Photo 1). There are numerous nursing pillows on the market that aid in correcting this postural dysfunction (Photo 2). Sometimes, multiple pillows may need to be used for increased comfort. There is no one correct way to hold the baby, so different positions should also be attempted in order to identify which is the most comfortable.
Even with postural support and correction, looking down at their new little love is unavoidable. This posture leads to increased strain on the posterior neck and upper back muscles while the muscles in the front of the neck and shoulders are placed in a shortened position, causing them to lose flexibility over time. These postures that have been adapted need to be counteracted in order to reduce or eliminate pain and dysfunction. An exercise routine that emphasizes restoring postural balance is key.
The following list of exercises is generally appropriate for clients who complain of postural pain related to breastfeeding. However, if the pain is severe, or does not improve with the following exercises, referral to a women's health physical therapist is in order. The patient should feel better after completing the exercise. If an increase in pain occurs, she is likely performing the exercise incorrectly or the exercise is not appropriate for the cause of her pain.
Chest openers and biceps combo stretch:
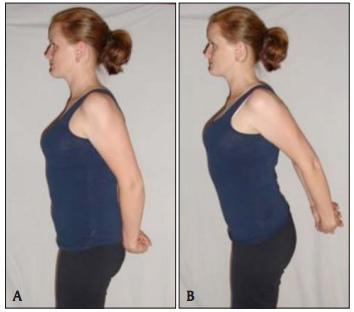
Cue the client to clasp her hands as pictured (A). Inhale, lift the shoulders down and back. Exhale, maintain that posture in the shoulders and lift the arms up (B). This stretch is intense, and should be broken down into 3 sets of 15 seconds for your client's comfort. This stretch should be performed after each feeding.
Neckstretch series:
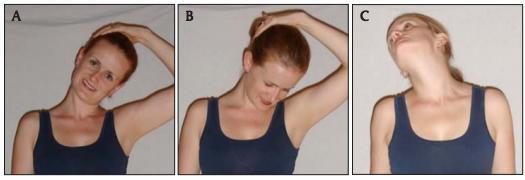
Cue client to first tilt her ear to her shoulder as pictured (A). Then, client should rotate her head down and to the side (B). Finally, the client should tilt her up and away (C). Each position should be held for 30 seconds and repeated twice each side. Additionally, this series should be performed at least 2 times per day.
Seated rows with resistance tubing:
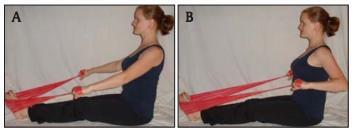
Cue the client to inhale and extend her spine into an upright position (A). Then, have her exhale as she pulls her arms, like she is rowing a boat (B). Perform 2 sets of 15 repetitions, 3 times a week. This exercise can also be performed without resistance.
Prone flies over birthing ball:
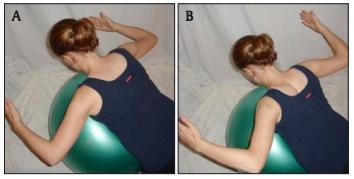
Position your client as above (A) and have her inhale to prepare. Then cue her to exhale as she lifts her arms up to the ceiling (B). She should begin with at least 10 repetitions and gradually work up to 30 repetitions before adding any weight. Creating a balance between strength and flexibility is key.
If a client's symptoms do not improve with the above techniques and exercises, additional intervention may be required. A women's health physical therapist can assist you with finding other potential causes of pain and provide a more directed treatment plan. If you don't know of one in your area, contact the American Physical Therapy Association Section of Women's Health at
