Help for Pubic Symphysis Pain
International Journal of Childbirth Education. June 2009.
Heather Jeffcoat, DPT
Pubic symphysis pain, or anterior pelvic girdle pain, is one of a myriad of musculoskeletal pains that women may experience during pregnancy. This pain can be debilitating, requiring some women to use crutches or a rolling walker to alleviate the pain while allowing some mobility. Some studies report that up to 50% of pregnant women have some type of pelvic girdle pain prior to 20 weeks gestation. Additionally, this pain negatively affects perceived health and sexual life during pregnancy (Mogren, 2006).
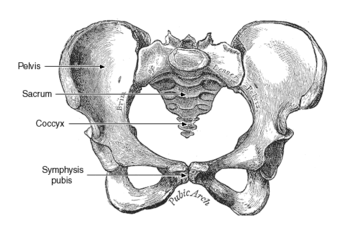 Pubic symphysis pain is defined as mild to severe pain over the pubic symphysis, and can extend down into the groin and medial thighs (unilateral or bilateral). It generally presents clinically as pain with standing (especially on one leg), prolonged sitting, or with transitional movements such as going from a sitting to a standing position, rolling over in bed, or going up or down stairs. In some women, there may be a clicking in the joint present.
Pubic symphysis pain is defined as mild to severe pain over the pubic symphysis, and can extend down into the groin and medial thighs (unilateral or bilateral). It generally presents clinically as pain with standing (especially on one leg), prolonged sitting, or with transitional movements such as going from a sitting to a standing position, rolling over in bed, or going up or down stairs. In some women, there may be a clicking in the joint present.
Oftentimes, this pain is present along with other types of pain, most commonly with lower back or sacral pain. One study pointed to additional physical and psychosocial factors that may increase risk of pubic symphysis pain during pregnancy, such as increased weight and less job satisfaction (Albert et al, 2006). Risk factors that are associated with prolonged pelvic pain at six months' time include increased BMI and pelvic joint hypermobility (Mogren 2006).
A study published earlier this year looked at pelvic girdle pain (including anterior or pubic symphysis pain) and disability reported in pregnant women in the first trimester and again at gestation week 30 (Robinson et al, 2010). Clinical examinations were also performed. The results showed that self-reported pain locations in the pelvis, a positive posterior provocations test and the sum of pain provocation tests present in early pregnancy are statistically significant with disability reports at 30 weeks gestation, but the number of pain sites is not.
Another study looked at hormonal contraceptive use and the occurrence of all types of pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain (Kumle et al, 2004). It found that the use of hormonal contraceptives was only significant with regards to pelvic girdle pain for the first pregnancy. The most significant determinant of pelvic girdle pain in subsequent pregnancies is the presence of pain in a previous pregnancy. Studies have looked at several factors to identify risk in developing various types of pelvic girdle pain, but there is no single factor that appears to play the biggest role. Once the pain occurs, there are some exercises your client can perform that may alleviate her symptoms.
Modifications in your client's daily activities are an essential first step to alleviate pain and pressure in the pubic symphysis. Instruct her to keep her legs together when she is rolling over in bed or getting out of the car, like she is wearing a tight mini-skirt. Also, it is generally more comfortable for her to get into bed "on all fours" and then lying on her side, rather than sitting in bed and lifting her legs up.
Additionally, there are some exercises your client can perform, which have been shown to reduce pubic symphysis pain (Depledge et al, 2005).
Exercises
- Abdominal Stabilization: Instruct your client to gently pull her navel towards her baby.
- Kegels: Instruct your client to contract her pelvic floor gently, like she is closing the openings.
- Gluteus Squeezes: Instruct your client to gently squeeze the buttocks. This can be done while standing.
- Lat Pulls: Instruct your client to grasp a door handle and gently pull it toward her.
- Adductor Squeezes: Instruct your client to place a small, soft ball between her knees and squeeze gently.
The good news is that pubic symphysis pain usually resolves on its own after birth. However, if the pain worsens or these initial exercises do not work, there are additional exercises and treatments your client can learn or receive from an experienced Women's Health physical therapist. To locate one in your area, go to www.womenshealthapta.org or call (800) 999-APTA extension 3229.
Related Search Terms:
- climbing stairs
- symphysis pubis dysfunction spd
- chronic pain
- hip pain
- pubic symphysis dysfunction
- pelvic bone
- pelvic girdle pain pgp
- symptoms of spd
- pubic bones
- front of the pelvis
References
Bump, et al. Assessment of Kegel pelvic muscle exercise performance after brief verbal instruction. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Aug;165(2):322-7
Carriere, B., Feldt, C.M. 2002. The Pelvic Floor. New York: Thieme.
Di Benedetto, P., Coidessa, A., Floris, S. Rationale of pelvic floor muscles training in women with urinary incontinence. Minerva Ginecol. 2008 Dec;60(6):529-41.
Hay-Smith, E.J., Dumoulin, C. Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Jan 25;(1):CD005654.
Stephenson, R., O’Connor, L. 2000. Obstetric and Gynecologic Care in Physical Therapy. New Jersey: Slack, Inc.
