
Understanding Clogged Milk Ducts and Non-Infectious Mastitis: A Comprehensive Guide
Breastfeeding is a meaningful and rewarding experience, but it can come with challenges—including clogged milk ducts and non-infectious mastitis. These conditions can cause discomfort,

Treatment Options for Postpartum Pelvic Pain Therapy in Los Angeles, CA
Bringing a baby into the world is an incredible physical and emotional experience. Yet for many new mothers, the weeks and months after childbirth can

Crunches for Diastasis Recti Abdominus (DRA): To Crunch Or Not To Crunch?
Are Crunches for Diastasis Recti Abdominus a Good Idea? Let’s Discuss. What does the most recent evidence say about the best exercises to rehab from

How Orgasm Improves Postpartum Pelvic Floor Function
Learn How Orgasm Improves Postpartum Pelvic Floor Function Try a naturally occurring strengthening method Many factors come into play when considering resuming to sexual activity

Negotiating Physical Activity for Perinatal Mental Health
Negotiating Physical Activity for Perinatal Mental Health Exercise is commonly prescribed as one method to help improve one’s mental health (Ekkekakis 2013, Hu et al

Coping Mechanisms for Sexuality Changes Postpartum
Sexuality Changes Postpartum Are Common Sexual Function After Childbirth Can Be Restored With These Tips In my last blog post, we explored the barriers many

Barriers to Restoring Sexual Function After Childbirth
Why Sexual Function After Childbirth Can Be a Challenge Disclaimer: This blog post is based on research performed on cis-gendered women Many women are told

Postpartum Sexuality & Mood Changes in Women with Pelvic Girdle Pain
Does my pelvic girdle pain have anything to do with my mood and sexuality? Many of our patients experience sexual dysfunction and anxiety, depression and

What do Breastfeeding Women Need and Want? – No One Told Me About This Part!
What do Breastfeeding women need and want? Let’s take a closer look. You’ve had your bundle of joy and you’re working out the kinks of

Babywearing 101: Benefits, Challenges, and Solutions for Caregivers
What is babywearing? Babywearing is the practice of transporting a baby or child in a sling or carrier that is worn on the body –

Commonly Linked: Urinary Incontinence and Postpartum Depression
What’s the Link Between Urinary Incontinence and Postpartum Depression? Postpartum Depression is a medical illness that negatively affects how you feel, the way you think,

Blog: A Safe Return to Running and Impact Activities in Postpartum
During pregnancy, the body goes through tremendous changes that can significantly impact strength, endurance, and ability to absorb ground reaction forces that are required to

Therapeutic Breast Massage in Lactation (TBML)
Therapeutic Breast Massage in Lactation Can Help Make Breastfeeding Less Painful Breastfeeding is widely accepted as the normal standard for providing nutrition to newborns, however,
The Effects of Pelvic Floor Muscle Strength on Orgasm
Let’s Look at the Effects of Pelvic Floor Muscle Strength on Orgasm Hint: strong pelvic floor muscles = strong orgasm The world is learning more

How to Manage Urinary Incontinence After Childbirth | Postpartum Recovery Series – Part 5
Postpartum Recovery Series Part 5 Managing Urinary Incontinence After Childbirth Urinary incontinence is the unwanted leakage of urine, also known as accidental bladder leakage. There

Incontinence During Pregnancy & Postpartum | Postpartum Recovery Series – Part 4
What causes incontinence during pregnancy? There are many causes for incontinence during pregnancy and postpartum. Some of the proposed factors are: hormonal changes, pelvic floor

Restless Legs Syndrome & Physical Therapy | Postpartum Recovery Series – Part 3
Restless Legs Syndrome (or RLS) Restless legs syndrome (or RLS) is a condition where there are uncontrollable urges to move limbs (mostly in the legs,

Diastasis Rectus Abdominis: What, Why, How? | Postpartum Recovery Series – Part 2
What is DRA? Diastasis rectus abdominis (DRA, sometimes referred to as Diastasis Recti) is a distortion or thinning of the linea alba which is the

Safely Returning to Activity and Sport | Postpartum Recovery Series – Part 1
afely Returning to Activity and Sport Postpartum Postpartum Recovery Part 1 Most women get the clearance after their 6 week check-up for sex and exercise,

Can A Vaginal Birth Ruin Your Sex Life? | Femina PT Talks Postpartum Sex
Are You Wondering “Can A Vaginal Birth Ruin Your Sex Life?” Medically, the answer is a resounding ‘no’… but postpartum sex is still an understandable

POP Quiz About Two Common Postpartum Conditions – Pelvic Organ Prolapse and Urinary Incontinence
What are Pelvic Organ Prolapse and Urinary Incontinence? What is the biggest risk factor for both conditions? And how can you tell if you have

How Physical Therapy Can Help with Clogged Milk Ducts and Mastitis
Physical therapy can help women across their lifespan. This includes support with orthopedic considerations related to breastfeeding, as well as other breastfeeding care with clogged

Vaginal Childbirth Positioning Series | Part 3: Delivery of the Placenta
Third Stage of Childbirth: Delivery of the Placenta You made it! Now, at this point you have delivered your baby and your body’s hormones have

7 Tips for Returning to Running Postpartum
Are You Thinking of Returning to Running Postpartum? There is not a magic time frame as each person recovers differently and the most important thing

5 Things You Can do to Improve Postpartum Pelvic Health
Postpartum Pelvic Health Recovery Should Start Day 1. Here are some tips to help you get your postpartum pelvic health (and general health) back on

Getting Back to Exercise Postpartum
A healthy lifestyle includes getting back to exercise postpartum Exercise has shown to be beneficial in all stages of life, and the postpartum period is
Mommy Tummy – Not Something You Have to Just Live With
Mommy tummy aka diastasis recti abdominis (DRA) is a prevalent issue. One in three American moms have DRA that persists greater than a year. So

How Is Your Running Changed After Childbirth?
What studies say about returning to running as postpartum exercise Most of the therapists in our office are moms, and we intimately understand wanting to

Sex After Childbirth – What’s Your ‘New Normal’?
You counted down the weeks until your baby’s arrival… now you and your partner are counting down the days until your doctor gives you the

Postpartum Anal Incontinence
What is Anal Incontinence? Anal Incontinence is defined as the complaint of involuntary loss of liquid or solid stool or the involuntary loss of gas.

Common Postpartum Issues That Make Sex Painful – and What You Can do About Them
Many women experience lower libido, vaginal dryness, sore muscles, and tender skin in the genital area after childbirth. These issues can make sex uncomfortable, or

Postpartum Pelvic Pain and What You Can Do About It
Pelvic pain during the postpartum period is common, even for those who had a “perfect and easy” pregnancy, labor and delivery. Often times, healthcare providers

Ghostpartum | Advocating for Proper Postpartum Care
Proper Postpartum Care is Crucial to Prevent “Ghostpartum” Today we are addressing “Ghostpartum,” which may sound like a Halloween ghoul or goblin, but is actually

Spin the Right Way with the Help of a Therapist
Spin The Right Way for Optimal Results! Want to start a spin class? Afraid of returning to cycling because of knee pain or pelvic pain?

Redefining Postpartum Care in the “Fourth Trimester”
Redefining Postpartum Care in the “Fourth Trimester” by Utilizing Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy Last month the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) updated their

Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy after Cesarean Section
What Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy after Cesarean Section Can Do For You Physical therapy after cesarean section can help you in your recovery by giving
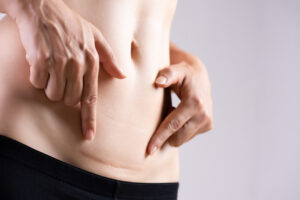
Scar Management and Desensitization After C-Section, Hysterectomy, and Laparoscopic Procedures
Tips For Scar Management and Desensitization After C-Section Also After Hysterectomy and Other Laparoscopic Procedures After delivery via cesarean section, hysterectomy or other laparoscopic procedure,

Cesarean Section Early Recovery Exercises
Learn To Do Cesarean Section Early Recovery Exercises It’s Cesarean Section Awareness Month! Trauma to the body is something all who give birth to a

Ergonomics with Baby Care and Self Care After Cesarean Section
Self Care After Cesarean Section, With an Emphasis on Baby Care Ergonomics Today we talk about ergonomics with baby care after a cesarean section. It’s important

